Understanding Stressers and DDoS-for-hire Services
Discover the role of stressers in modern network resilience testing.
Stresser Techniques: IP Spoofing
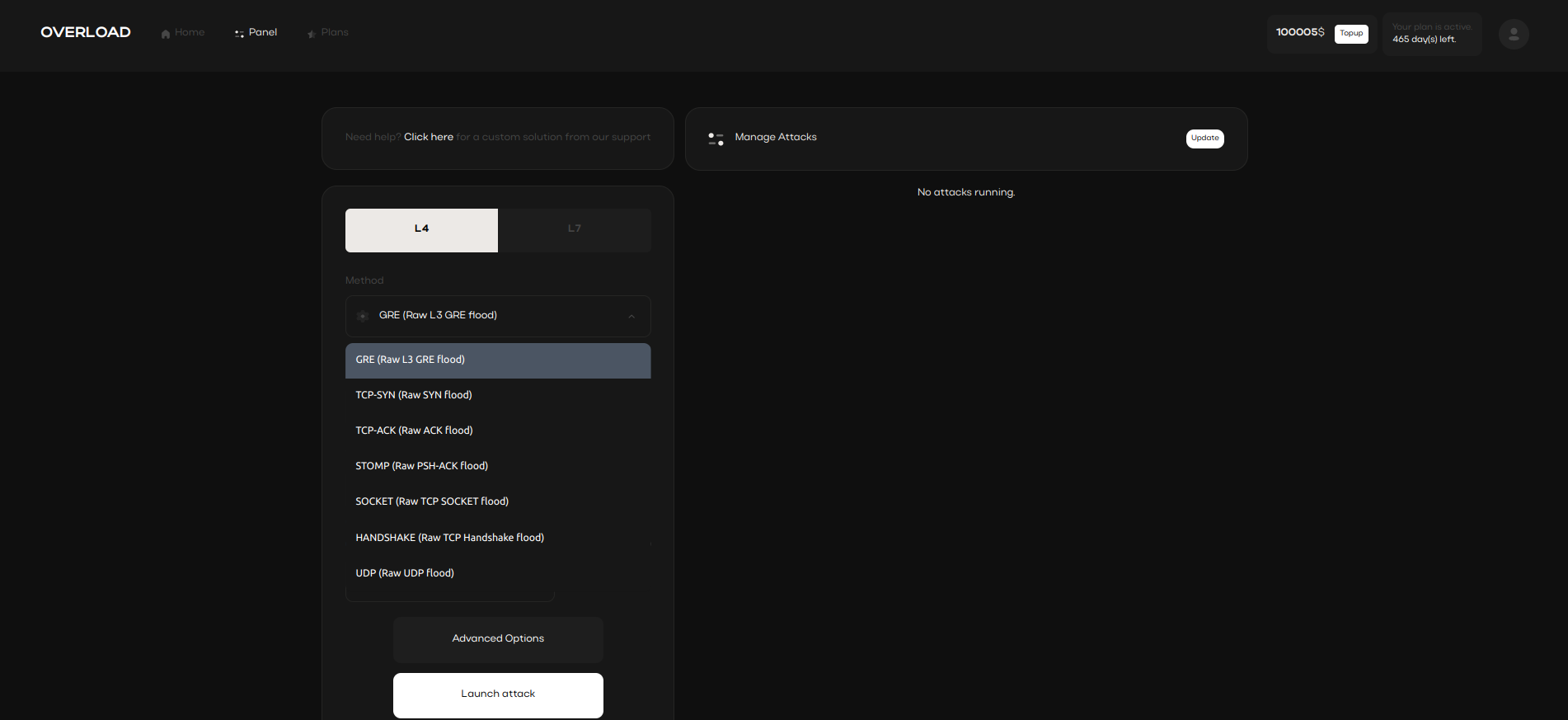
Network Layer 4 (L4) attack methods, commonly utilized in IP stressers, chosen specific network protocols to overwhelm servers.
One popular technique is identity masking, where the attacker’s real IP address is hidden, making it difficult to trace.
These L4 methods and identity masking tactics are frequently applied to bypass basic firewall protections protections
and effectively simulate high traffic loads on a chosen server.
Exploring Booter Services

In addition to stressers, there are also booters
which serve a similar purpose. Booters are often used to simulate high traffic loads and identify security gaps in systems.
These Distributed Denial of Service applications allow for a distinctive understanding of server durability. However,
misuse of booter services can lead to permitted issues due to unauthorized network attacks.
Understanding Stresser Services
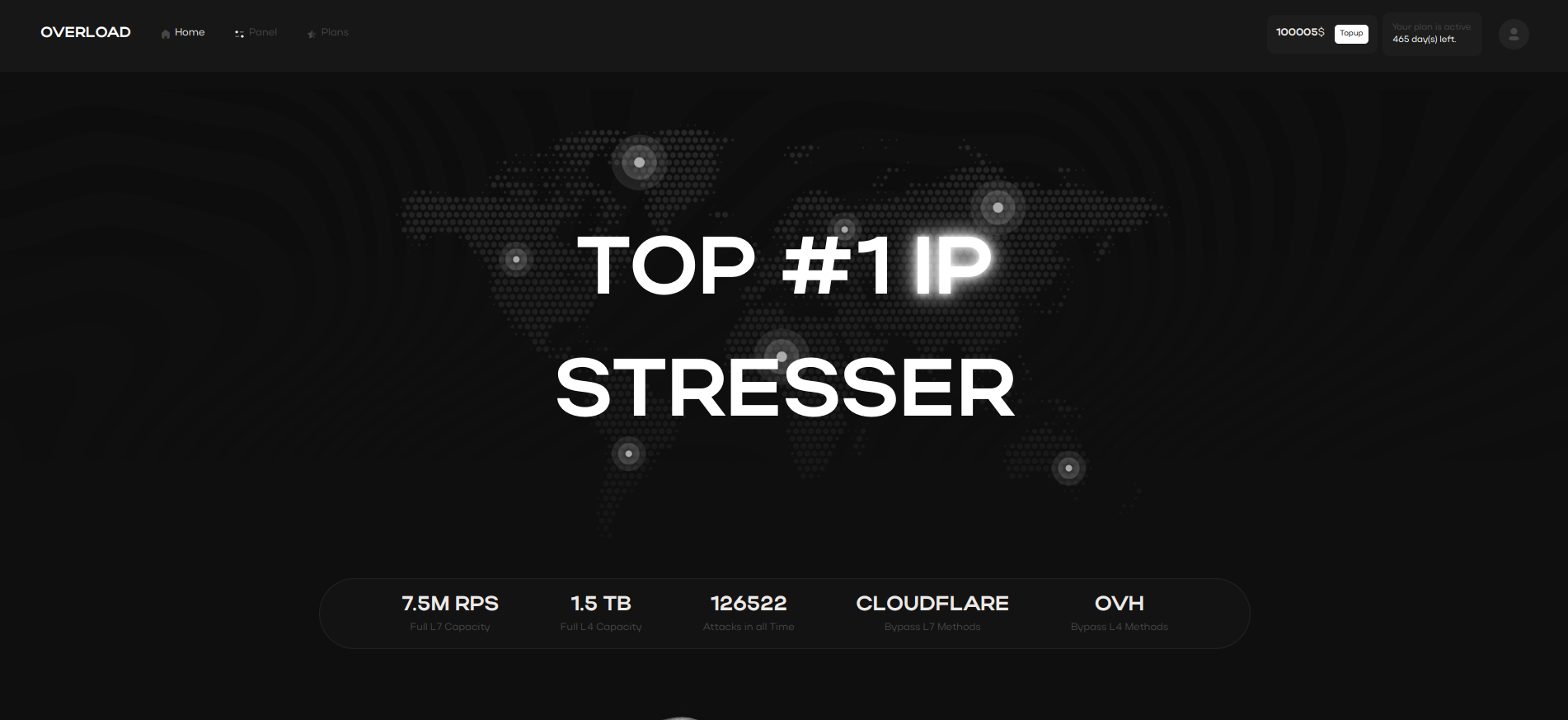
Online services designed to test the resilience of servers under
load called Stresser. They are specifically used to simulate traffic flood attacks to check the protection of websites and servers. However,
some users exploit stressers to launch unauthorized traffic flood attacks on sites
and applications, which is considered unlawful.
The ip stressers market involves renting out such services, allowing users
to initiate attacks on selected targets. This type of service often attracts attention due to its controversial nature,
and it is essential to understand all legal aspects and potential risks.
DNS/NTP/CLDAP Amplification Attacks

address spoofing attacks can be enhanced through various reflection-based techniques, such as CLDAP, NTP, DNS boost.
These methods allow attackers to send small commands and receive significantly larger returns, amplifying the attack’s impact.
By using address spoofing tactics, the attack origin is masked, making it challenging to trace
and prevent the traffic from overwhelming the target’s system.
- DNS reflection method
- NTP boost method
- CLDAP traffic magnification
